| .. | ||
| images | ||
| shaders | ||
| CMakeLists.txt | ||
| hello_vulkan.cpp | ||
| hello_vulkan.h | ||
| main.cpp | ||
| README.md | ||
Callable Shaders - Tutorial
 Author: Martin-Karl Lefrançois
Author: Martin-Karl Lefrançois
Tutorial (Setup)
This is an extension of the Vulkan ray tracing tutorial.
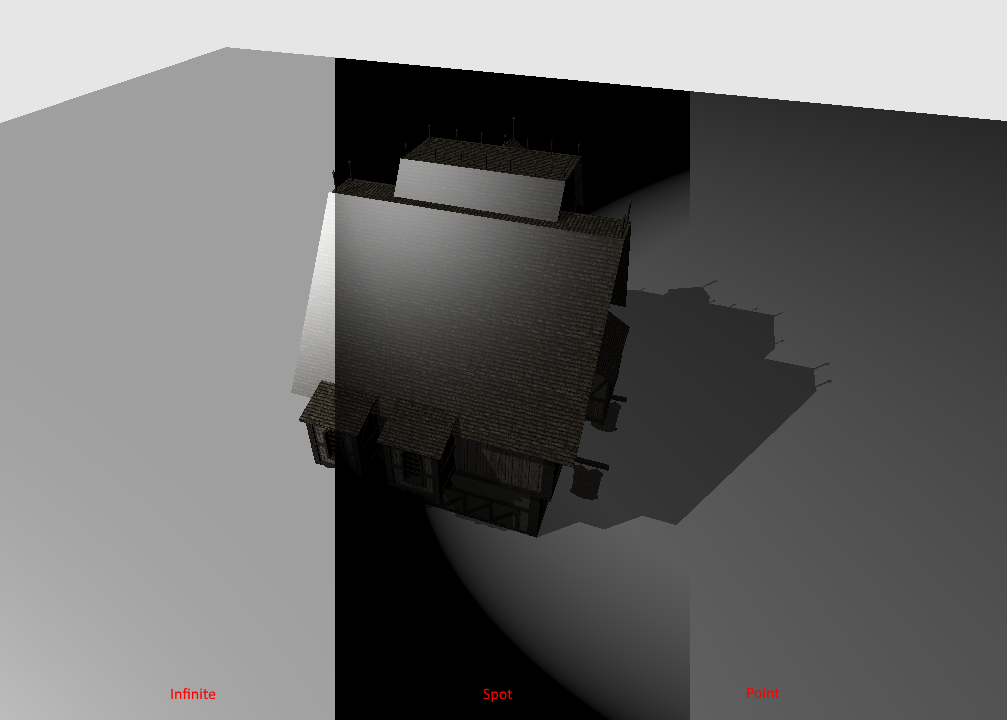
Ray tracing allow to use callable shaders in ray-generation, closest-hit, miss or another callable shader stage. It is similar to an indirect function call, whitout having to link those shaders with the executable program.
(insert setup.md.html here)
Data Storage
Data can only access data passed in to the callable from parent stage. There will be only one structure pass at a time and should be declared like for payload.
In the parent stage, using the callableDataEXT storage qualifier, it could be declared like:
layout(location = 0) callableDataEXT rayLight cLight;
where rayLight struct is defined in a shared file.
struct rayLight
{
vec3 inHitPosition;
float outLightDistance;
vec3 outLightDir;
float outIntensity;
};
And in the incoming callable shader, you must use the callableDataInEXT storage qualifier.
layout(location = 0) callableDataInEXT rayLight cLight;
Execution
To execute one of the callable shader, the parent stage need to call executeCallableEXT.
The first parameter is the SBT record index, the second one correspond to the 'location' index.
Example of how it is called.
executeCallableEXT(pushC.lightType, 0);
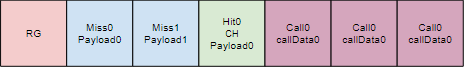
Adding Callable Shaders to the SBT
Create Shader Modules
In HelloVulkan::createRtPipeline(), immediately after adding the closest-hit shader, we will add
3 callable shaders, for each type of light.
// Callable shaders
vk::RayTracingShaderGroupCreateInfoKHR callGroup{vk::RayTracingShaderGroupTypeKHR::eGeneral,
VK_SHADER_UNUSED_KHR, VK_SHADER_UNUSED_KHR,
VK_SHADER_UNUSED_KHR, VK_SHADER_UNUSED_KHR};
vk::ShaderModule call0 =
nvvk::createShaderModule(m_device,
nvh::loadFile("shaders/light_point.rcall.spv", true, paths));
vk::ShaderModule call1 =
nvvk::createShaderModule(m_device,
nvh::loadFile("shaders/light_spot.rcall.spv", true, paths));
vk::ShaderModule call2 =
nvvk::createShaderModule(m_device, nvh::loadFile("shaders/light_inf.rcall.spv", true, paths));
stages.push_back({{}, vk::ShaderStageFlagBits::eCallableKHR, call0, "main"});
callGroup.setGeneralShader(static_cast<uint32_t>(stages.size() - 1));
m_rtShaderGroups.push_back(callGroup);
stages.push_back({{}, vk::ShaderStageFlagBits::eCallableKHR, call1, "main"});
callGroup.setGeneralShader(static_cast<uint32_t>(stages.size() - 1));
m_rtShaderGroups.push_back(callGroup);
stages.push_back({{}, vk::ShaderStageFlagBits::eCallableKHR, call2, "main"});
callGroup.setGeneralShader(static_cast<uint32_t>(stages.size() - 1));
m_rtShaderGroups.push_back(callGroup);
And at the end of the function, delete the shaders.
m_device.destroy(call0);
m_device.destroy(call1);
m_device.destroy(call2);
Shaders
Here are the source of all shaders
Passing Callable to traceRaysKHR
In HelloVulkan::raytrace(), we have to tell where the callable shader starts. Since they were added after the hit shader, we have in the SBT the following.
Therefore, the callable starts at 4 * progSize
std::array<stride, 4> strideAddresses{
stride{sbtAddress + 0u * progSize, progSize, progSize * 1}, // raygen
stride{sbtAddress + 1u * progSize, progSize, progSize * 2}, // miss
stride{sbtAddress + 3u * progSize, progSize, progSize * 1}, // hit
stride{sbtAddress + 4u * progSize, progSize, progSize * 1}}; // callable
Then we can call traceRaysKHR
cmdBuf.traceRaysKHR(&strideAddresses[0], &strideAddresses[1], &strideAddresses[2],
&strideAddresses[3], //
m_size.width, m_size.height, 1); //
Calling the Callable Shaders
In the closest-hit shader, instead of having a if-else case, we can now call directly the right shader base on the type of light.
cLight.inHitPosition = worldPos;
//#define DONT_USE_CALLABLE
#if defined(DONT_USE_CALLABLE)
// Point light
if(pushC.lightType == 0)
{
vec3 lDir = pushC.lightPosition - cLight.inHitPosition;
float lightDistance = length(lDir);
cLight.outIntensity = pushC.lightIntensity / (lightDistance * lightDistance);
cLight.outLightDir = normalize(lDir);
cLight.outLightDistance = lightDistance;
}
else if(pushC.lightType == 1)
{
vec3 lDir = pushC.lightPosition - cLight.inHitPosition;
cLight.outLightDistance = length(lDir);
cLight.outIntensity =
pushC.lightIntensity / (cLight.outLightDistance * cLight.outLightDistance);
cLight.outLightDir = normalize(lDir);
float theta = dot(cLight.outLightDir, normalize(-pushC.lightDirection));
float epsilon = pushC.lightSpotCutoff - pushC.lightSpotOuterCutoff;
float spotIntensity = clamp((theta - pushC.lightSpotOuterCutoff) / epsilon, 0.0, 1.0);
cLight.outIntensity *= spotIntensity;
}
else // Directional light
{
cLight.outLightDir = normalize(-pushC.lightDirection);
cLight.outIntensity = 1.0;
cLight.outLightDistance = 10000000;
}
#else
executeCallableEXT(pushC.lightType, 0);
#endif